Capturing the volatile compounds of the breath directly on the absorbent tubes, allows the analysis by thermal desorption and avoids the complex and laborious steps of sample preparation.
The backflush capability of Markes’ TD instruments allows for multiple bed tubing and traps, expanding the range of compounds that can be reliably monitored from a single sample.
The main challenges associated with breath analysis relate to the low concentrations of many compounds of interest and the complexity of the breath, in addition, respiratory profiles vary significantly between individuals and are influenced by numerous factors including diet, age, gender, medications and physical activity.
The natural variation among the healthy population makes it more difficult to identify robust biomarkers, that is, compounds or groups of compounds that can be used reliably to distinguish between healthy individuals and those with a certain pathology or condition.
Other factors that complicate breath analysis include: the huge number of samples required to conduct a study, their high intrinsic humidity, and the frequent need to store samples long-term before an entire batch can be analyzed together.
The latest generation of Markes xr thermo desorber series incorporates advanced TD technologies to address these challenges, making the TD-GC / MS analytical technique the “gold standard” for breath analysis.
These technologies gave birth to Mistral: the innovative method based on breath analysis that allows the early and non-invasive diagnosis of numerous diseases, developed by the research work of the University of Bari and Predict.
The project starts from breath analysis: the science that analyzes the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) present in the breath.
Through a simple puff, Mistral stores the compounds contained in the breath in an adsorbent tube. The tubes arrive at the Mistral Lab for sample analysis and characterization, using Markes-Agilent TD-GC / MS technologies distributed by SRA Instruments.
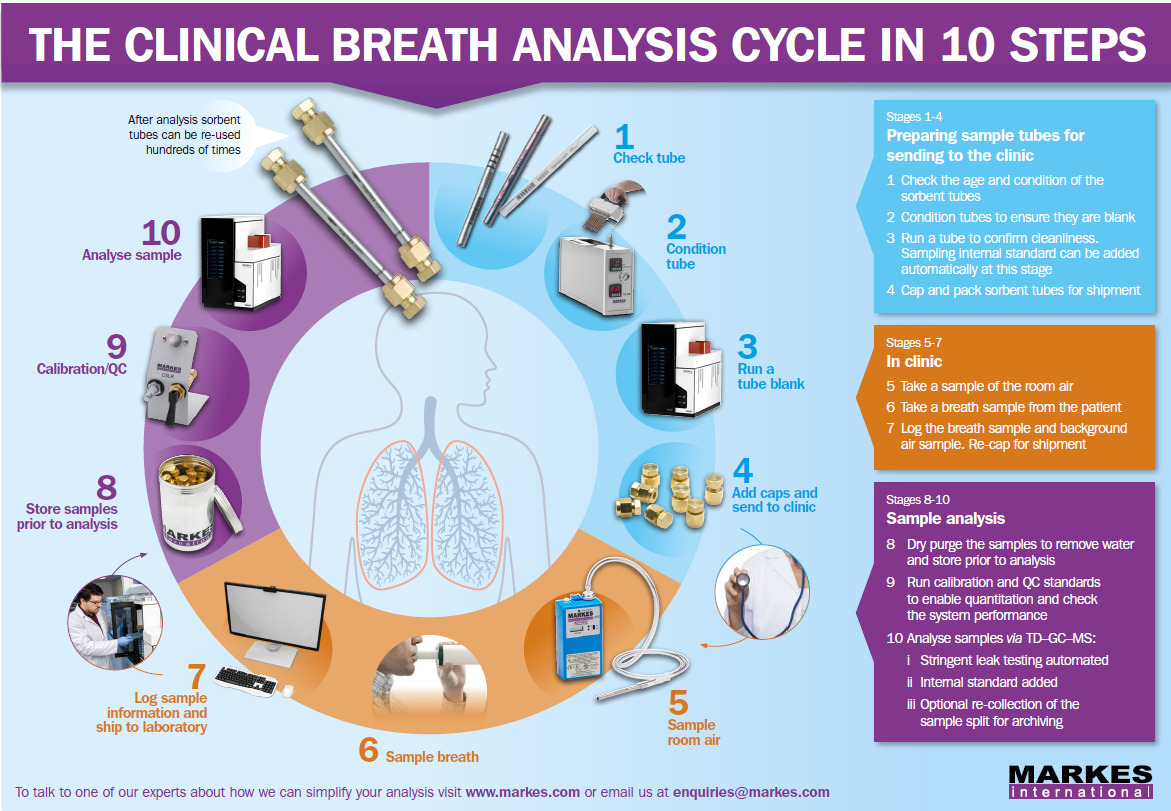
Optimising the analytical performance of sorbent tube sampling and thermal desorption–GC–MS for disease diagnosis via breath and bio-monitoring
This application note is intended to provide guidance on optimising the analytical performance of thermal desorption (TD) for those carrying out routine or research monitoring of breath for disease diagnosis. It summarises the major steps in the sampling and laboratory workflow, identifies the main analytical challenges and advises on which features and parameter ranges to select.