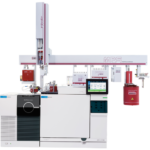
Full automation of the sample preparation and analysis process
Current EU legislation provides for objective criteria aimed at classifying the various types of olive oils (virgin, clear, refined, etc.).
These criteria are explained by the Delegated Regulation (EU) 2022/2104 and 2022/2105 of 29 July 2022.
Assigning each oil to the correct class it belongs to is of fundamental importance for:
- guarantee the commercialization of olive oils that meet the characteristics declared on the label
- avoid potential adulteration, even of a malicious nature, ultimately protect the health and interests of the final consumer.
The regulation define the analytical methods relating to the quantification of the parameters of interest; many of these involve laborious sample preparation, large quantities of solvents and consumables, as well as the use of qualified operators for a long time.
SRA Instruments, in collaboration with the Sas Biochemical Analysis Center, has conducted an in-depth study of the methods in use, coming to offer the market a series of analytical solutions based on the Gerstel GmbH platform, able to fully automate the sample-prep phases, resulting in savings in terms of time, solvent and materials.
The robotic stations developed are able to fully automate the sample preparation process and subsequent analyzes aimed at determining, respectively, the content of:
- alkylesters and waxes –Download the application note below
- sterols, triterpene dialcohols and aliphatic alcohols – Download the application note below
- stigmastadienes – Download the application note below.
The use of robotic stations also allows you to greatly limit the possibility of incurring random errors, as well as keeping the process under control by inserting a large number of QCs within a batch; in this way, not only high productivity is guaranteed, but also an extremely reliable final data in terms of precision and accuracy.
The portfolio of SRA solutions for the analysis and characterization of oils includes:
- Determination of MOSH and MOAH in just 30 minutes – Saponification included in the workflow. References: ISO Method 20122/2024 – JRC 2023 technical report: Determination of MOSH and MOAH in edible oil.
- 2D speciation of MOSH/MOAH with GC×GC-FID/QTOF
- Determination of 3-MCPD and Glycidol in Edible Oils – Automate the entire range of AOCS Methods Cd 29(a,b,c,d)_13
– Regulatory reference: Commission Regulation (EU) 2020/1322 of 23 September 2020.
Alkylesters and waxes: full automation of the sample preparation and analysis process
Characterization of olive oils in accordance with EEC regulation 2022/2014-2015. Fully automated analysis of sample preparation.
The guiding principle of the solution consists in the elimination of offline preparative techniques (LC, LLE), replacing them with an automated separation of the fractions of interest via HPLC. Specifically, the accurate optimization of the chromatographic parameters makes it possible to make the elution times of the various classes extremely repeatable.
Sterols, aliphatic alcohols and triterpene dialcohols: Full automation of the sample preparation and analysis process
Characterization of olive oils in accordance with EEC regulation 2022/2014-2015. Fully automated analysis of sample preparation.
The guiding principle of the solution consists in the elimination of off-line preparative techniques (LC, TLC, LLE), replacing them with an automated separation of the fractions of interest via HPLC.
Specifically, the accurate optimization of the chromatographic parameters makes it possible to make the elution times of the various classes of aliphatic alcohols and sterols / triterpene dialcohols extremely repeatable.
Automation includes the initial saponification process.
Stigmastadienes: full automation of the sample preparation and analysis process
Characterization of olive oils in accordance with EEC regulation 2022/2014-2015. Fully automated analysis of sample preparation.
The guiding principle of the solution consists in the elimination of off-line preparative techniques (LC, TLC, LLE), replacing them with an automated separation of the fractions of interest via HPLC. This analytical approach also allows to eliminate the saponification step.